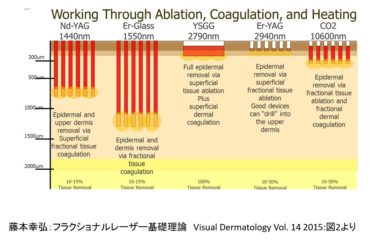
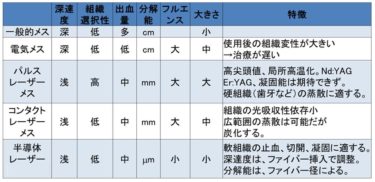
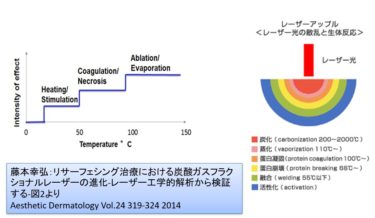
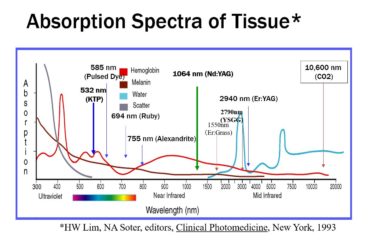
Management Strengthening Measures for Beauty-Related Medical Clinics
Takahiro Fujimoto, MD, PhD, MBA ClinicF Tokyo Japan
Introduction
This paper is a revised version of the content presented at the 34th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Aesthetic Surgery, under the lecture category of “Risk Management.” The original presentation was titled “Management Strengthening Measures for Hospitals, Including Corporate Conversion of Medical Institutions and Anti-aging Treatment.”
Currently, the healthcare system in Japan faces various problems such as the national health insurance system and increased healthcare costs, mixed insurance and medical care, shortage of doctors and uneven distribution of medical specialties, medical fee system, medical quality and malpractice, and more. However, these problems are not unique to Japan; they exist in various countries worldwide, even with different systems. When considering national healthcare policies, the essential elements of cost, quality, and access are emphasized. However, since these three elements compete with each other, it is difficult to achieve them all simultaneously. In Japan, healthcare costs are among the lowest of advanced countries, and access to healthcare is guaranteed by the national health insurance. As for medical quality, it can be said that it is maintained at a certain level primarily through the efforts of physicians.
Modern Western medicine has developed by investigating the cause of newly arising diseases and developing treatment methods, including drugs and medical devices, to overcome them, with the focus on treating patients with diseases to bring them closer to a healthy state. Consequently, while the importance of preventive medicine, which protects healthy individuals from chronic diseases, such as lifestyle diseases, has been emphasized recently, it has received less attention in the past.
Based on the above, this paper discusses peripheral topics related to independent beauty-related medical clinics and their management strengthening measures. For convenience, this paper uses the term “beauty clinic” to refer to beauty-related medical clinics, “beauty doctor” to refer to physicians involved in beauty-related fields, and “beauty treatment” to refer to the treatment provided by beauty clinics.
1. Features of Beauty Treatment
(1) Preventive Medicine, Maintenance and Promotion of Beauty and Health
The “Health Japan 21” campaign, which is being promoted by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, aims to “realize a reduction in mid-life mortality, an extension of healthy life expectancy, and an improvement in quality of life.” It emphasizes “further promotion of primary prevention, which focuses not only on early detection or treatment by medical checkups, which has been the center of conventional disease measures but also on the promotion of health and the prevention of disease.” Thus, national policies related to health aim to reduce physical illnesses, improve mental health, and promote health and beauty. Beauty treatment is expected to contribute to preventive medicine, which is essential for maintaining health, and to promote the maintenance and promotion of beauty and health.
(2) Specificity of Aesthetic Medical Treatment
As of the end of 2010, the number of doctors in Japan was 280,431 (180,966 in hospitals and 99,465 in clinics), showing an increase of about 15.3% over the past 10 years. Although the number of cosmetic surgeons is relatively small compared to the total number of doctors, there were 427 at the end of 2010 (21 in hospitals and 406 in clinics), which is about twice the number 10 years ago. However, since cosmetic surgery is included in the field of plastic surgery, which deals with the surface and shape of the body, the actual number of aesthetic doctors is expected to be much higher, and it is expected to increase in the future, including those who switch from other specialties.
However, since medical education at university medical schools still focuses on the treatment of diseases, there are few opportunities to learn medical techniques for those who aspire to become aesthetic doctors. Due to their lack of experience, there is a risk of medical malpractice, among other things. Furthermore, since most aesthetic medical treatments are based on elective procedures, hospitals tend to handle them less frequently, and small clinics are the main providers. In addition, medical devices used for medical purposes in aesthetic treatments, such as photo-laser treatment equipment, have advanced rapidly in technology, and the investment required to upgrade to more expensive models that provide higher treatment effects is significant. If the trend of an increase in doctors and a decrease in patients continues, there is a risk of financial difficulties in clinic management.
Thus, it can be said that aesthetic medical treatment is a unique field among medical specialties.
On the other hand, while there are no accurate statistics on the attributes of patients undergoing aesthetic medical treatment, since most of these procedures are elective and non-urgent, the number of patients is believed to be influenced by their income level. In other words, if the current economic downturn continues, there is a tendency to reduce spending on aesthetic medical treatment, and latent demand is expected to decrease.
(3) Types of Aesthetic Medical Treatments
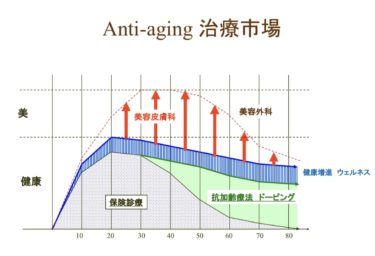
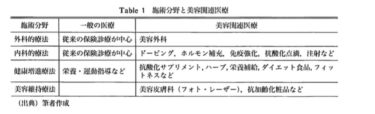
Although there are many types of aesthetic medical treatments, they can be classified by the type of procedure, as shown in Table 1. In addition to cosmetic surgery, which was previously the mainstream, there has been an increase in internal medicine treatments such as doping therapy, hormone replacement therapy, immune enhancement, antioxidant drips, injections, which do not require as much expertise. Relatively new fields include health-promoting therapies that use supplements, foods, herbal medicine, enzymes, etc., to supplement nutrition, exercise, and rest. Furthermore, there has been an increase in aesthetic dermatology treatment centered on treatment with photo-laser devices, which have made rapid technological progress over the past decade. The reason why the table uses the term “maintenance therapy” is that while other therapies are transient, meaning that when the treatment is completed, the patient’s visits usually end, maintenance therapy is a continuous therapy that aims to maintain the achieved aesthetic results.
2. Business Strategy of a Cosmetic Clinic
As a medical corporation, a cosmetic clinic is subject to non-profit constraints. In other words, legally, it is required not to engage in “activity aimed at profit.” However, even if it is non-profit, to maintain and improve the quality and safety of medical care through sufficient investment in facilities and human resources and to stabilize management, it is necessary to secure an appropriate financial foundation. Furthermore, in the future, as mentioned above, it is expected that there will be an excess supply of doctors and clinics compared to demand (number of patients), so there is an increasing trend to introduce the concept of for-profit business management while prioritizing mission fulfillment at cosmetic clinics.
While business administration is primarily a field of study that aims to construct theories with a long-term perspective for efficient and effective operations in for-profit enterprises, when applied to cosmetic clinics, it leads to researching methods (strategies) to gain appropriate profits to maintain and stabilize management and to invest in the latest knowledge and expensive medical equipment. Until now, many cosmetic clinics and their physicians in charge have felt that management is important in the back of their minds, but they have often been too busy with treatment to consciously incorporate strategies, and it cannot be said that many clinics have consciously incorporated strategies. For example, when opening a new cosmetic clinic, it is important to conduct market analysis, set up a proper concept, consider specific strategies to achieve that concept, decide on resource allocation methods, and execute tactics distinguishing long, medium, and short-term goals. However, if the marketing strategy is left to others, staff education and financial management are also done in a rough way, it is unlikely to be successful. The following presents some of the management strategies that should be introduced in cosmetic clinics based on the author’s experience.
(1) Concept Development
Even if a cosmetic clinic boasts of treating cosmetic issues, it is difficult to address all patients and all symptoms, and there is no uniqueness or creativity in terms of external image, and the treatment results may not be satisfactory in cases where it is not their forte. In cosmetic clinics with many individual practitioners, it is believed that disclosing the most proficient treatment and dedicating oneself to that specialty can lead to credit assurance, an increase in repeat patients, and a decrease in errors. If the treatment results are good, patients will be evaluated and become repeat customers, and as a result, new patients will increase through word of mouth. For example, there is a medical form called “Medical Focused Factory” that has been attracting attention in the United States recently. This is a form in which physicians who are specialists in treating diseases such as cancer, heart disease, foot diseases, hernias, etc., concentrate on treating only one type of disease, and the number of cases treated increases, making it possible to achieve high treatment results. Therefore, in order to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of cosmetic clinics, it is necessary to establish a clear concept and specialize in specific treatments.
Opening a beauty clinic requires a clear concept regarding the type of patients to target, the field of treatment, and the specific treatments or procedures to offer. In the service industry, market segmentation involves classifying customers based on various criteria and promoting or selling services tailored to their specific characteristics. Similarly, when opening a beauty clinic, it is essential to analyze and determine the attributes of the target patients, such as age, location, and income level, while considering Table 1 as a reference to clearly define the clinic’s strengths in terms of treatment fields, diseases, and treatment methods.
Moreover, if the clinic targets beginners who have never visited a beauty clinic like a, the concept should prioritize educating and providing thorough guidance to beginners, including insurance-covered treatments. On the other hand, if the clinic targets patients who have already experienced beauty clinics, such as b, they need to consider strategies and tactics such as b-1 attracting patients from competing clinics to win over competition or b-2 offering additional treatments that the patients cannot receive at other clinics.
(2)Patient retention is essential to a beauty clinic as patients can easily choose to visit other clinics if they are dissatisfied. To increase patient satisfaction and retention, the clinic should implement measures such as clearly explaining the expected effects of treatments and how to maintain beautiful skin, allowing patients to choose treatment methods, using equipment that can explicitly demonstrate the effects, and providing post-treatment care guidance.
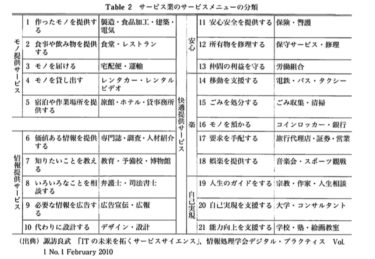
In addition, since the service industry accounts for about 70% of Japan’s current industrial structure, it is essential to thoroughly examine the nature of services provided. Researchers from various fields are combining efforts to study services from a multidisciplinary perspective, given that the majority of IT industry operations are now service-oriented.
(3)Furthermore, it can be said that all services provided by a cosmetic clinic are applicable to providing comfort, but the most important service is the patient’s self-realization menu. Patients have expectations beforehand, and satisfaction increases when their treatment results meet those expectations, leading them to want to return. Conversely, if their expectations are high but their results are evaluated poorly, they will be disappointed and the clinic will lose the patient. Additionally, a patient’s expectations naturally increase over time, so it is necessary to carefully communicate honestly, confirm treatment details and expected results in order to guide their expectations to their proper level. To increase patient satisfaction and provide them with an experience that impresses them with the results of the treatment, it is important to bring their inflated expectations back to a reasonable level and allow them to enjoy self-realization.
In this way, it is desirable for a cosmetic clinic to satisfy all the service elements of goods, information, and comfort, so efforts should be made to make up for any missing elements. However, providing goods requires funding, and providing information requires time to obtain the latest information through domestic and international academic activities. Therefore, the quickest service to provide is the comfort service, and within that, it is desirable to have a variety of self-satisfaction menus.
(4) Comfort Service and Staff Education
There are many factors that make patients feel favorable towards a cosmetic clinic, or in other words, increase their satisfaction. Of course, the most important factors are the patient’s trust in the physician’s knowledge and skills and the treatment results, but it is not an exaggeration to say that all services provided from the moment they enter the clinic until they leave are also related. However, the service referred to here does not mean manners (behavioral rules to avoid making patients feel uncomfortable), but hospitality (consideration for patients and heartfelt hospitality). Manners that show well-behaved behavior without offending the patient can usually be manualized, but hospitality, which means showing consideration that brings patients closer and creates a sense of intimacy, or the service that goes beyond what the patient is looking for, is difficult to manualize because it requires discerning each patient’s type and timing. Even if it could be manualized and carried out exactly as written, it would not impress the patient.
As for the elements that make patients feel comfortable, there are hardware aspects such as the location of the clinic, the building, the interior, and medical equipment, as well as human attractions such as the clinic director’s knowledge, skills, personality, and familiarity. However, in order to make patients feel hospitality, it is important for the staff’s actions and attitudes to be considered. To instill the spirit of hospitality that cannot be manualized in the staff, it is important to establish and disseminate the philosophy and service concept of the clinic, to make the staff proud and have pride, to create a mechanism for collecting patient needs, and to accumulate ingenuity in the field. In particular, it is most important to make the staff proud and have pride, and the physician as the manager should always talk and act with the attitude of “providing the best service to patients” in staff meetings, enlightening the staff’s consciousness and inspiring pride and ambition.
(5) Understanding patient needs
In a beauty clinic where customers are somewhat selected, it is considered more suitable to recognize and understand the differences in each customer’s values, needs, and treatment history, and to approach each one individually according to their individual needs (One-to-One Marketing). For example, in order to respond to a customer’s order at a beauty salon or bar such as “as usual,” it is necessary to grasp each customer’s preferences and habits. In a beauty clinic, in addition to questionnaires, medical records, and invoices, staff should create a character note for each patient, record what was talked about during treatment, such as preferences for food, fashion, and shopping, things to be careful about, preferences, and disliked words, etc., and read it before the patient comes in, in order to provide hospitality that matches the patient’s needs.
3.The Future of Aesthetic Clinics Management
Under the system of elective medical treatments, patients have the freedom to choose their medical institution and treatment method, and pay for it themselves. Except for medical underserved areas where no other clinics exist, it is clear that patients will not go to clinics that do not provide any benefits in fiercely competitive metropolitan areas, as mentioned above. Therefore, let’s consider what we can do for the future management of aesthetic clinics.
(1) Introduction of Anti-Aging Medicine
The elderly population (age 65 and over) in Japan has rapidly increased from approximately 29.4 million in 2010 to 35.9 million in 2020, and is expected to continue increasing gradually or stay flat until around 2050. Among them, more than 80% are healthy elderly people who do not require care. However, although they are healthy, they have a higher incidence of illness and worries about health and illness compared to younger people. Anti-aging medicine, which aims to maintain and manage health and counter aging, is a topic of interest to elderly people who are conscious of their appearance and physical strength and want to delay the progression of aging.
According to the Japan Anti-Aging Medical Society, anti-aging medicine is defined as “the theoretical and practical science aimed at enjoying longevity in good health” and is considered a very broad concept, emphasizing that it is “the ultimate preventive medicine focused on aging.” Note that it is inevitable for human physical and mental functions to decline with aging. Therefore, as mentioned above, the author wants to view anti-aging medicine not as a medicine that prevents diseases but from the perspective of “maintaining health or beauty” or “delaying progression.” In other words, just as beauty medicine is a medical treatment that focuses on appearance and “maintaining beauty,” anti-aging medicine also focuses on appearance and “maintaining health and beauty.”
Many for-profit companies have already made various attempts to enter the huge anti-aging market of 80% of the elderly population, but fortunately, aesthetic clinics have experienced many treatments and methods related to anti-aging, including skin diseases such as spots, sagging, wrinkles, and dark circles, and have many overlaps with the concept of anti-aging medicine. Therefore, for aesthetic clinics that are forced to endure unstable management, entering the new market of anti-aging medicine can be expected to raise their management foundation.
(2) Hospital Corporatization
Under current legal systems, it is not possible to establish a new corporate hospital. However, there are cases where corporations indirectly participate in hospital management by leasing hospital land, facilities, and equipment to doctors, for example. As mentioned above, it is considered difficult for corporations to enter hospitals that are primarily focused on insurance medical care, but it can be said that there is a foundation for realizing the entry or conversion of corporations into beauty clinics, especially those with a business model that is primarily focused on private medical services and is similar to profit-oriented service industries.
Summary
Until a few decades ago, medical services in Japan were largely controlled by doctors, and patients had to rely on them and follow their orders. However, as education levels have increased and more women have entered the workforce, patients have become more demanding of medical services that are more rational and efficient in terms of time and money. As a result, patients have started to seek more information about their illnesses and suitable medical facilities. Medical books and know-how related to medical care are available in bookstores, and the internet is overflowing with information on the causes, symptoms, progress, treatment methods, side effects, and so on of various diseases. As a result, the asymmetry of information between doctors and patients is gradually disappearing, and patients are becoming able to choose medical facilities that are suitable for them. Therefore, it is said that competition is intensifying in beauty clinics, particularly because patients have a lot of freedom to choose medical facilities and treatment methods. As a result, there is a risk of bankruptcy for clinics that operate without proper management.
Here, we introduce some of the management know-how used in profit-oriented service industries in beauty clinics and attempt to explain it with several examples based on the author’s experience. Furthermore, since anti-aging medical care is promising in the future and overlaps with the treatment and care provided in beauty clinics, we have discussed the possibility of entering the field of anti-aging.
Finally, it should be emphasized that until now, the role of medical institutions has been primarily to discover and treat diseases, which has been considered legitimate. However, the field of health maintenance and promotion has tended to be considered beyond the scope of medical care. Moreover, the government is focusing more on preventive medicine rather than health maintenance in order to respond to the increasing burden of medical expenses. On the other hand, with the increasing number of women in the workforce and the aging of society, the demand for medical care focused on “maintaining health and beauty” has been increasing. Therefore, it is necessary for medical institutions to take on new roles and to provide high-quality medical services that meet the changing needs of patients.
藤本幸弘;美容関連診療所の経営強化策、日本美容外科学会会報、第35巻、第1号、平成25 (2013)3月p32−p39 翻訳版